by Dr. Jacqueline S. Allen | Apr 22, 2021 | Blog, Endodontics, Endodontist, Phoenix Endodontic Group, Root Canal
For many years, comedians have regularly used the term “root canal” to capture any painful experience. The jokes weren’t funny to anyone who actually needed a root canal – fear of pain was sometimes enough to keep them from getting badly needed care.
Today’s root canals, though, have advanced dramatically in terms of technique and technology from 20 or even 10 years ago. In many cases, a root canal now relieves dental pain, instead of intensifying it.
Your endodontist is trained in pain management for root canals and other procedures that involve the roots and nerve pulp of your teeth. The amount of discomfort you experience during and after a root canal will vary with your individual circumstances, but here are some of the most common factors that can impact your pain level.
What Factors Influence Root Canal Pain?
- The amount of infection in or damage to the tooth prior to the procedure. Root canals are performed on teeth with infected, inflamed, or damaged tooth pulp. One common symptom of tooth pulp damage is persistent tooth pain. If your tooth is badly infected before your root canal, it can also be more sensitive afterward.
- How you use pain relievers after your root canal. Some tenderness and sensitivity is expected after the procedure. Your endodontist can provide guidance on when to take over-the-counter pain relievers and what kind of dosing schedule to maintain until the pain is no longer a distraction.
- How closely you listen to and follow post-procedure instructions from your endodontist. After your root canal, you will want to avoid chewing with the affected tooth until it has received a permanent dental restoration (typically a crown). You will also want to choose soft, cool foods like applesauce or yogurt to eat for the first few days. Hard, hot, or crunchy foods increase the likelihood you will feel sensitivity or pain when you eat.
- How quickly you report any severe post-procedure pain. It’s imperative you call your endodontist right away if you experience sharp or severe pain after your root canal; this can indicate that infection has returned. You will need to be seen to assess the situation, and your endodontist can plan additional pain and infection management steps.
“Today’s root canals rarely involve severe pain,” says Dr. Allen, who practices at the Phoenix Endodontic Group. “Your endodontist is your partner in managing discomfort after a root canal and is the first person you should call if that pain becomes severe.”
by Dr. Jacqueline S. Allen | Feb 22, 2021 | Blog, Endodontics, Endodontist, Phoenix Endodontic Group, Root Canal
While more and more Americans are becoming aware of the benefits of preserving natural teeth, you may still find yourself with a number of questions and no little anxiety when a root canal is the suggested option for saving a diseased or damaged tooth. Root canals can be an intricate procedure, depending on the extent of the damage to the tooth. Occasionally, sedation is called for. However, most of the time, patients are awake during the procedure and fully aware of each step the endodontist is taking. Each case is different, though, so let’s look at the issue a little more broadly.
How Endodontists Manage Pain And Patient Awareness During Root Canals
- For most root canals, local anesthesia is used to numb the area around the affected tooth. This is a necessary step because your endodontist will be removing pulp and nerve fibers from your tooth. You will likely be fully awake during the entire procedure. Your mouth, including your lips, may feel numb for several hours after the procedure, so it is important to be careful if you eat or drink before full feeling returns to the numbed area. Be sure to follow your endodontist’s guidelines for eating and drinking, though.
- For patients with dental anxiety or dental phobia, some level of sedation may be necessary for the root canal to be a success. Sedation can range from minimal (just to take the edge off your jitters) to deep (where you may be barely conscious, but able to be awakened). It can be delivered by inhalation, orally, or intravenously. General anesthesia – during which you are completely unconscious – is rarely used for root canals and requires special training to safely administer.
Dr. Allen, of the Phoenix Endodontic Group, encourages patients to discuss questions related to wakefulness and anxiety with their endodontist during the planning stages of their root canal. “In our practice, we make sure all our patients are fully informed and arrive ready for their root canal,” she says. “We can discuss your individual needs prior to beginning the procedure and offer solutions that will help you feel comfortable, safe, and pain-free.”
by Dr. Jacqueline S. Allen | Dec 21, 2020 | Blog, Endodontics, Endodontist, Root Canal
It’s crucial to have accurate information when considering a root canal. A qualified general dentist or endodontist can offer up-to-date knowledge about how root canals work and why you might need one.
Here are five common root canal questions received at the Phoenix Endodontic Group.
5 Top Root Canal Questions – Answered.
- What symptoms indicate a root canal may be needed? Natural teeth that are candidates for root canals have typically been damaged by decay or infection, or suffered structural damage to the tooth. Symptoms that may call for a root canal include: a severe toothache when you chew or apply pressure to the affected tooth; prolonged sensitivity to hot or cold; a recurring pimple on the gums near the tooth; discoloration of the tooth; swelling or tenderness in adjacent gum tissue.
- Will a root canal hurt? Today’s root canal procedures typically relieve pain created by infection or damage to the nerves inside the tooth pulp, rather than causing pain. Additionally, endodontists receive special training in pain management, so even post-operative discomfort is typically minimal.
- Is a root canal a better option than having my tooth pulled? The answer to this question depends on the overall health of your tooth, the gums surrounding it, and whether other natural teeth are suffering advanced decay or infection. One noteworthy advantage to retaining your natural teeth is a reduced chance of bone loss in your jaw. Such loss can lead to a host of negative consequences.
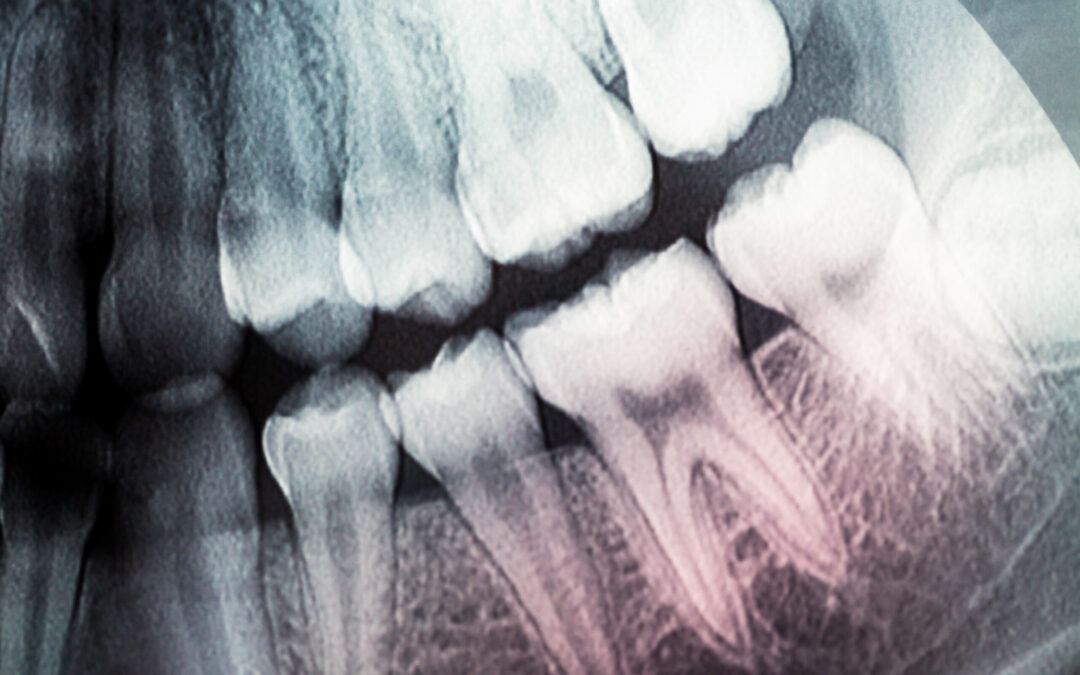
- What happens during a root canal? Here is a brief overview of how a root canal is performed: First, your endodontist will take X-rays. Then, they will numb the area with a local anesthetic and place a dental dam over the tooth to protect it from bacteria. Next, the practitioner will drill an access hole in the crown of the tooth. The pulp chamber and roots of the tooth will be thoroughly cleaned, shaped with special tools, then filled with a biocompatible material. Once complete, the endodontist covers the opening with a temporary filling. Weeks later, the final step in the procedure takes place: placing a crown, permanently sealing the access hole.
- Does it take a long time to recover after a root canal? Most patients experience some mild tenderness in the area of the root canal for a few days. This is usually managed with over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers. This discomfort should disappear within a week. If you experience severe pain, significant swelling, or if your temporary filling falls out, contact your endodontist as soon as possible so they can examine the tooth.
“It’s normal to be apprehensive if you have never had a root canal before,” says Dr. Allen, who practices with the Phoenix Endodontic Group. “Our office is always happy to answer your questions about root canals and provide you with a more comprehensive view of the procedure.”
by Dr. Jacqueline S. Allen | Oct 12, 2020 | Blog, Endodontics, Phoenix Endodontic Group, Root Canal
Many dental patients know that root canals can save natural teeth but may wonder what actually happens inside the tooth with the procedure. Of course, there are many benefits to retaining your natural teeth whenever possible. The root canal treatment procedure replaces the living nerve pulp of your tooth with an inert biocompatible material, usually gutta-percha. Here’s a quick look at how root canals impact your natural tooth and allow them to remain a part of your smile.

How A Root Canal Affects Your Tooth
- The root or nerve pulp. This is the part of a tooth’s anatomy most impacted by a root canal. Typically, a root canal is called for if the tooth nerve has died or if the pulp is badly infected. During a root canal, the nerve pulp is removed with special tools and the canals themselves are flushed with material to treat the infection, so it does not return.
- The dentin. This layer of calcified tissue supports the top layer of enamel in a natural tooth. Dentin is produced by nerve pulp, so once the pulp is replaced with gutta-percha, dentin will no longer be produced in that tooth, which may make your teeth more brittle.
- The enamel. This hard outer layer of your natural tooth protects the internal parts of your tooth. It can be compromised by tooth decay or dental injuries (cracked or broken teeth), allowing bacteria to invade your nerve pulp chamber. A root canal stops this process, because not only does it remove the infected nerve pulp, the finishing restoration – a crown – fits like a “cap” over the tooth enamel, protecting it from additional damage or bacterial intrusion.
- The periodontal ligament. Sometimes a tooth is damaged because it is pushed out of position, threatening the periodontal ligament, which attaches our natural tooth to the jaw. In this case, a root canal can prevent further damage to the tooth, allowing it to be splinted in place to encourage the periodontal ligament to reattach and preventing infection issues inside the tooth.
While root canals do not “kill” natural teeth, removing and replacing the nerve pulp makes the tooth more brittle. Your endodontist will determine if you need additional restorations beyond a crown to ensure your tooth has sufficient support to function normally.
“Root canals do change how your natural teeth function, but they allow the other structures that are part of your teeth and gums to return to health, supporting your overall oral wellbeing,” says Dr. Allen, who practices with the Phoenix Endodontic Group. “Our practice is always happy to explain precisely how endodontic treatment can help preserve your natural teeth.”

by Dr. Jacqueline S. Allen | Aug 23, 2020 | Blog, Endodontics, Endodontist, Root Canal
Root canal treatments are highly effective in saving injured or infected natural teeth. They are typically not lengthy procedures, but most laypeople are not clear on what’s involved in a root canal or what to look for when selecting a practitioner. If your regular dentist has recommended an endodontist perform your root canal, you will want to be fully informed and feel confident about your treatment. Here are some questions to help you prepare.

What To Ask Your Endodontist Before A Root Canal Treatment
-
What kind of equipment is used for root canals? Endodontists typically perform the procedure far more frequently than a general dentist, so they also have specialized equipment that make the process easier and faster. This equipment can also help better resolve unexpected challenges that may present themselves during the treatment.
-
Do I need to take antibiotics before my root canal treatment? If you have certain types of systemic health issues, including a past history of infective endocarditis, your endodontist may prescribe antibiotic prophylaxis to ensure that you are protected should any oral bacteria enter the bloodstream. If you have an abscess, antibiotics may also be called for. Discuss your entire health history with your endodontist when your root canal is in the planning stages.
-
How many visits will my root canal take? Most root canal treatments are done in a single session, but occasionally you will need to return for a second appointment to finish the procedure. If that’s the case, your endodontist will place a temporary filling to protect your tooth until the treatment is finished.
-
How soon should I make my root canal appointment? Your regular dentist may have already communicated some of your symptoms to the endodontist, and this may give them a rough idea of how soon you need to be treated. However, some symptoms of a serious tooth injury are only apparent after a thorough clinical examination by a specialist; even if you think your symptoms aren’t bothersome, you should make an endodontic appointment as soon as one is available.
-
What should I do if I experience pain after my root canal? Your endodontist should provide you with a pain management plan for the first few days after your treatment, when some discomfort is normal. This may include information on using cold packs or pain-reducing medication. If you experience moderate or severe pain after the third day following your procedure, call your endodontist to see if they would like you to come back in for a recheck.
“Endodontists welcome questions from patients before, during, and after a root canal treatment,” says Dr. Allen, who practices with the Phoenix Endodontic Group. “We want you to understand your case fully, and we will provide you all the information you need to be comfortable and confident about your procedure.”
by Dr. Jacqueline S. Allen | Jun 24, 2020 | Blog, Endodontics, Endodontist, Phoenix Endodontic Group, Root Canal
Root canals are often the treatment of choice when you develop a serious infection involving your natural tooth’s pulp, or if your tooth has been chipped, cracked, or otherwise damaged. However, while root canals have a high success rate and a high patient satisfaction rate, not every root canal ends up being a permanent solution.
The factors that initially bring a patient to the endodontist influence whether their tooth can be saved by a root canal. Here is a short list of conditions that can make saving a tooth with a root canal treatment more challenging.
 Factors That Can Interfere With Saving Natural Teeth With Root Canals
Factors That Can Interfere With Saving Natural Teeth With Root Canals
-
Teeth with long or unusually curved roots. Endodontists use special tools and seal the roots. If a patient’s canals are hard to clean, it may be less likely that the treatment will be permanently successful.
-
A crack in the tooth root. Even though teeth treated with a root canal are protected above the gum line with a restoration such as a crown, if the root itself develops a crack, infection can re-enter the tooth.
-
Advanced periodontal disease. Your gums play an integral role in your oral health and if you have severe or recurrent gum disease, saving your natural tooth through a root canal is far less likely to be successful.
-
Previous root canal treatment of the tooth. There are ways to treat a tooth if the original root canal fails, such as a retreatment or an apicoectomy. However, the success rates for additional procedures are not as high as for a first-time root canal treatment.
“Although root canal treatment often provides a lifelong solution for a damaged or infected natural tooth, it isn’t the best choice for every patient,” says Dr. Allen, an endodontist who practices with the Phoenix Endodontic Group. “Our staff can perform a thorough examination and advise you on your best treatment options.”






